Enhance Public Service Quality through ISO Standards

Improving Public Services with ISO 9001: Practical Certification for the Public Sector
Government organizations looking to lift service quality and trackable results increasingly turn to ISO 9001 as a proven framework for building, operating, and improving a quality management system (QMS). ISO 9001 uses a process-based model that links policy, operational controls, and performance measurement so agencies can meet stakeholder needs consistently and increase citizen satisfaction. As public expectations grow for transparency, faster service, and accountable procurement, ISO 9001 helps by standardizing workflows, formalizing management review, and promoting decisions backed by evidence. This guide explains how ISO 9001 and complementary ISO standards strengthen public services, maps standards to common compliance needs, outlines how AI-assisted auditing supports certification, and offers practical steps public organizations can follow — with help from accredited providers. You’ll come away with core ISO principles for government, which standards apply to everyday public functions, the role AI plays in audits, measurable KPIs, and a realistic path to certification for the public sector.
Why is ISO 9001 Essential for Public Sector Quality Management?
ISO 9001 matters for public-sector quality management because it gives agencies a structured QMS that ties organizational goals to consistent service delivery, continual improvement, and measurable outcomes. Its process approach ensures inputs, controls, and outputs are managed across administrative functions, producing predictable results that reduce variation and errors. For agencies, that often means faster processing, fewer complaints, and clearer audit trails that support budgetary and policy accountability. Seeing how these mechanisms work shows that ISO 9001 is more than paperwork — it’s a practical way to align leadership, resources, and operations around citizen-centered results. The sections that follow unpack the core principles and the concrete mechanisms that turn ISO 9001 requirements into better citizen experiences and operational efficiency.
What are the core principles of ISO 9001 for government agencies?
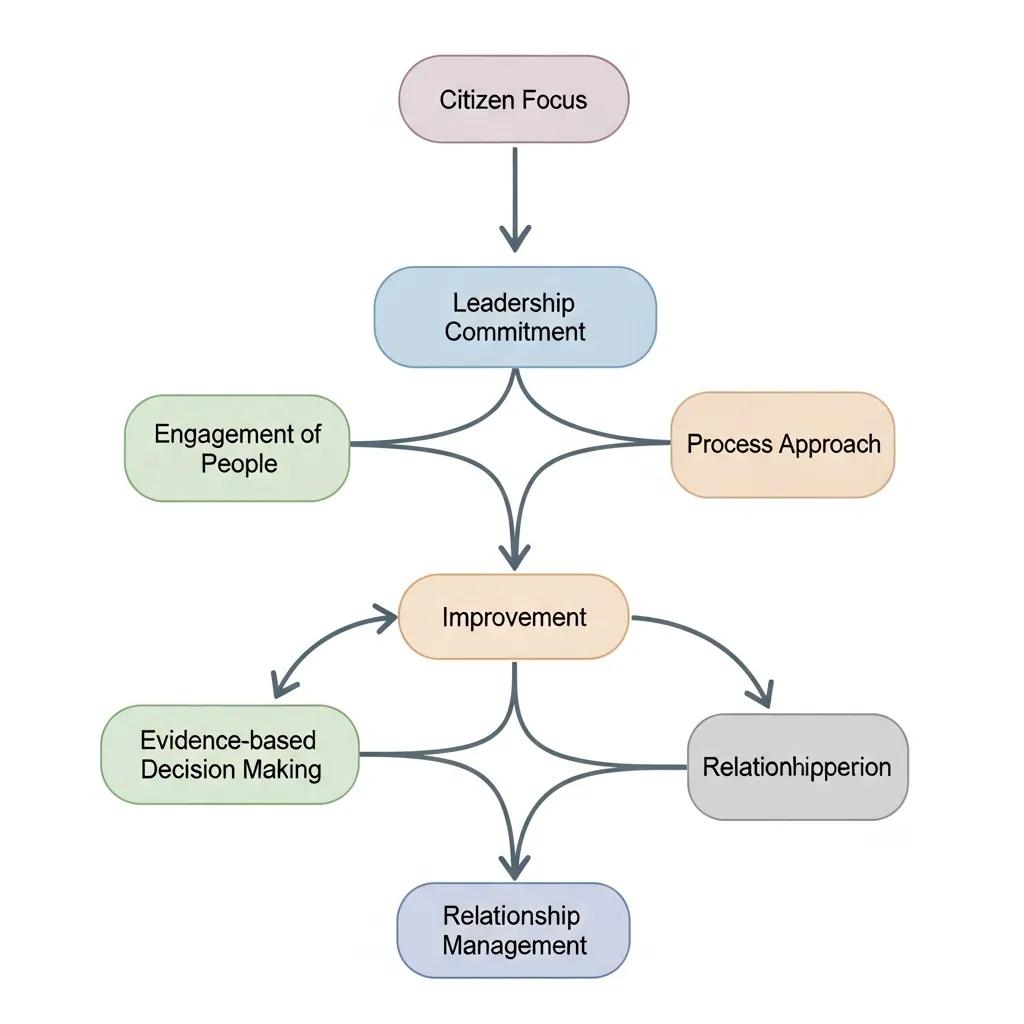
ISO 9001 frames quality management around a set of principles public agencies can adapt to both back-office and citizen-facing services: citizen (customer) focus, leadership commitment, people engagement, a process approach, continual improvement, evidence-based decision making, and relationship management. Citizen focus means mapping service journeys — for permits, benefits, or licenses — to remove friction. Leadership commitment ensures coherent policy and resource support across departments. The process approach standardizes procurement, records handling, and case management to reduce mistakes. Agencies put these principles into practice by documenting process ownership, setting measurable KPIs, training frontline staff on standard procedures, and using management review to prioritize improvements. When applied systemically, these principles create a reliable foundation for service delivery and prepare organizations for external certification audits.
- Mapping citizen journeys reduces rework and handoffs, improving throughput.
- Designating process owners clarifies accountability and speeds corrective action.
- Regular measurement and review cycles drive iterative improvements that support policy goals.
These examples naturally lead to how ISO 9001’s mechanisms convert into measurable improvements in citizen satisfaction and operational performance.
How does ISO 9001 improve citizen satisfaction and operational efficiency?
ISO 9001 improves citizen satisfaction by making services predictable, responsive, and measurable. It boosts efficiency by cutting variability and waste. Techniques like process mapping and controls shorten the time to complete routine transactions, while feedback loops and corrective actions reduce repeat errors and complaints. Typical KPIs include average processing time, first-contact resolution rate, complaint frequency, and satisfaction survey scores — agencies adopting QMS practices often report double-digit improvements in these measures within 12–18 months. For example, clear SOPs for procurement or licensing shorten approval cycles and create auditable records that support transparent decision making. Tracking these metrics feeds management review and continuous improvement, producing durable gains in both citizen experience and cost-efficiency.
These measurable effects highlight the broader role ISO and related standards play across government functions; the next section examines that compliance and accountability role.
How Do ISO Standards Ensure Government Compliance and Accountability?
ISO standards support compliance and accountability in government by requiring documented processes, defined responsibilities, and independent verification mechanisms that create consistent audit trails. Different ISO standards target different governance needs — quality management, information security, environmental stewardship — so agencies can select and combine standards that align with statutory and policy obligations. The standards call for records, management reviews, internal audits, and external certification audits, all of which create evidence for legislators, auditors, and the public that obligations are being met. Embedding these standards introduces predictable documentation flows and measurable controls that strengthen oversight, reduce fraud risk, and increase transparency. The following sections show which standards map to common public administration needs and how certification practices support risk management and open governance.
Which ISO standards apply to public administration quality improvement?
Several ISO standards are particularly relevant to public administration because they address common compliance domains: ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO/IEC 27001 for information security, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and other emerging standards for safety and information governance as required. ISO 9001 supports process reliability in citizen services and procurement; ISO/IEC 27001 protects citizen data and records; and ISO 14001 structures environmental programs and reporting for municipal services. Agencies often implement these standards in an integrated management system to reduce duplication and align controls across functions. Typical examples include secure records handling in social services under ISO/IEC 27001, standardized procurement and contract processes under ISO 9001, and sustainable waste-management programs under ISO 14001.
These mappings demonstrate how standards translate into concrete compliance attributes; the table below summarizes specific examples and ISO contributions to common compliance goals.
Different standards address distinct compliance requirements and together build a comprehensive accountability framework.
| Public Function | Compliance Attribute | ISO Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Procurement & Contracts | Transparency of decisions | ISO 9001 requires documented processes, evaluation criteria, and audit records |
| Citizen Data & Records | Confidentiality and integrity | ISO/IEC 27001 mandates risk assessments, access controls, and incident response |
| Environmental Services | Regulatory reporting & impact control | ISO 14001 structures objectives, controls, and monitoring for environmental programs |
How does ISO certification support transparency and risk management in government?
ISO certification strengthens transparency and risk management by requiring documented policies, internal audits, corrective actions, and management reviews that produce auditable evidence of controls and decisions. Certification bodies evaluate whether documented processes are actually applied, giving third‑party assurance that reduces information asymmetry between government and the public. Risk management becomes systematic: agencies identify risks (fraud, data breaches, service interruption), deploy controls, and measure effectiveness through KPIs and audit findings. Suggested KPIs for transparency and risk include the share of processes with documented controls, percentage of corrective actions closed on time, incident response time, and frequency of external audit findings.
These mechanisms both reduce operational and reputational exposure and create clear reporting lines for oversight bodies and citizens.
The accountability structures above also lay the groundwork for more efficient, evidence-driven certification workflows — increasingly augmented by AI-driven auditing tools that speed verification without sacrificing rigor.
What Role Does AI-Driven Auditing Play in Enhancing Public Service ISO Certification?

AI-assisted auditing complements traditional certification by automating evidence sampling, surfacing patterns and anomalies in large datasets, and freeing auditors to focus on substantive issues instead of routine checks. AI can parse transaction logs and sample thousands of records to flag outliers, trends, and incomplete documentation much faster than manual review, shrinking audit time and improving detection. For public-sector QMS audits — where procurement records, case files, and service logs can be extensive — AI improves both audit depth and efficiency. Responsible use requires governance for algorithmic transparency, bias mitigation, and human oversight so that findings remain accountable and explainable. The sections below quantify AI benefits and outline likely developments toward continuous auditing in government.
How does AI improve audit accuracy and reduce certification costs?
AI improves audit accuracy by applying pattern detection and anomaly scoring across large evidence sets, enabling auditors to prioritize high‑risk transactions and uncover subtle compliance gaps that manual sampling can miss. Features such as automated stratified sampling, trend analysis, and natural-language processing of policies and records expand coverage and reduce time spent on low-value tasks. Advanced providers report meaningful reductions in on-site audit time and faster report turnaround, which lower certification costs and shorten time-to-certification. Agencies using AI-assisted pre-audit scans can address nonconformities earlier, narrowing the scope of formal audits and accelerating corrective cycles. Below is a compact comparison of typical AI capabilities and their benefits.
Before adopting these capabilities, agencies should put in place clear data governance and ensure human validation of algorithmic findings to preserve trust and defendable results.
| Audit Area | AI Capability | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Review | Pattern detection & anomaly scoring | Targets high-risk cases, increases defect detection rate |
| Evidence Sampling | Automated, stratified sampling | Expands coverage and reduces manual sampling time |
| Documentation Analysis | NLP-based policy & record parsing | Speeds identification of missing or inconsistent records |
What is the future of AI auditing in public sector quality management?
In the near term, AI auditing will automate routine checks and speed evidence collection. In the medium term, expect continuous auditing and predictive compliance signals that flag emerging risks before they materialize. Long term, AI will likely integrate with digital government platforms so compliance signals flow from operational systems to auditors in near real time, enabling faster corrective action and more dynamic management review. Public trust and legal defensibility will hinge on governance: algorithmic transparency, bias detection, and auditability of AI outputs. Pilots that pair AI analysis with human contextual review offer a balanced approach that preserves accountability while capturing efficiency gains.
Stratlane Certification is an accredited certification body providing ISO 9001 services designed for public organizations. We combine traditional audit rigor with AI-assisted evidence sampling and pattern analysis to shorten audit cycles, improve systemic defect detection, and reduce client time and cost. Accredited across multiple jurisdictions and serving governments, SMEs, corporations, and academic institutions in the US, EU, and UK, Stratlane focuses on clear deliverables and certificate management so agencies can sustain continuous compliance and produce auditable records for stakeholders. This mix of accreditation and technology helps public clients achieve timely, cost-effective certification while keeping independent verification front and center.
With that capability overview, we turn to the measurable benefits government agencies typically realize after certification.
What Are the Tangible Benefits of ISO Certification for Government Agencies?
ISO certification delivers concrete benefits for government agencies: cost savings, operational improvements, stronger public trust, and procurement advantages tied to verified processes. Standardization reduces waste and rework, management review directs resources to high-impact fixes, and certification signals to partners and citizens that the agency operates under auditable controls. Comparative case evidence shows measurable operational savings and improved satisfaction scores; the table below summarizes typical municipal outcomes and value ranges to set realistic expectations. These improvements support better budget use and help agencies compete for grants or partnerships that require certified management systems.
How does ISO 9001 certification lead to cost savings and operational improvements?
ISO 9001 drives cost savings through process standardization, waste reduction, and continual improvement that eliminate non-value activities and cut rework. Typical mechanisms include clarified roles, streamlined approval paths, fewer procurement exceptions, and earlier detection of bottlenecks. Core KPIs to monitor are process throughput time, rework rate, cost per transaction, and the share of corrective actions closed on time; improvements in these areas frequently translate to 15–30% operational savings in targeted functions. Agencies usually start with a gap analysis and focused pilots — for example, speeding permit issuance or claims processing — to prove early returns before scaling improvements across departments.
To illustrate likely benefits across common public entities, the table below sets out expected value ranges from certification efforts.
| Entity | Outcome | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Municipal Council | Operational cost saving | 15–30% in targeted processes |
| Licensing Office | Processing time reduction | 20–40% faster cycle times |
| Social Services Unit | Complaint reduction | 25–50% fewer repeat complaints |
In what ways does ISO certification build public trust and enhance accountability?
ISO certification builds trust by offering independent validation that processes are controlled, transparent, and under continual review. It strengthens accountability through required records, management review, and documented corrective actions.
Certification also gives agencies a clear way to report verified performance improvements to citizens and oversight bodies. Effective communication tactics include publishing summary audit outcomes, KPI dashboards, and plain-language explanations of how certification changed citizen-facing procedures. When certification is paired with proactive transparency, technical compliance becomes a visible public benefit — reinforcing legitimacy and stakeholder confidence.
These public-facing advantages drive demand for efficient certification paths; the next section explains how organizations can pursue certification with Stratlane.
How Can Public Sector Organizations Achieve ISO Certification with Stratlane?
Stratlane Certification offers a practical route for public organizations to secure ISO 9001 by combining accredited assessment services with AI-assisted audit tools and certificate management. Our approach focuses on scoping the QMS to the agency’s public functions, conducting a gap analysis, implementing corrective actions, running AI-supported audits to sample and analyze evidence efficiently, and then issuing certification followed by ongoing certificate management. Stratlane’s model is backed by accreditation in 27+ countries, so agencies operating across jurisdictions can rely on consistent assessment criteria and internationally recognized certificates. Below is a step-by-step outline agencies can adapt to their context and timelines.
The numbered list below summarizes the practical phases of certification and what agencies should prepare at each stage.
- Scoping and initial assessment: Define which services and processes will be in the QMS and gather baseline process documentation.
- Gap analysis and planning: Identify nonconformities, assign process owners, and create a corrective action plan with timelines.
- AI-assisted audit preparation: Run automated evidence sampling and document parsing to surface gaps before the formal audit.
- Certification audit and corrective action: Complete the external assessment, close findings, and receive certification once requirements are met.
- Certificate management and continual compliance: Maintain records, conduct internal audits, and use certificate management services to schedule surveillance audits and renewals.
This stepwise path accelerates readiness and uses AI to reduce audit time while preserving the independent verification that builds public trust.
The next subsection highlights brief case summaries that show measurable outcomes from AI-enabled certification engagements.
What is the Stratlane Certification process for public sector ISO 9001?
Our certification process starts with an initial scoping workshop to map critical services and concludes with certificate issuance and ongoing management support. AI tools streamline evidence collection and analysis throughout. Typical timelines depend on scope but commonly range from 3 to 9 months for single-function pilots, with concurrent corrective action work shortening calendar time. Client commitments include supplying documented processes, granting access to records for evidence sampling, and sponsoring internal resources to implement fixes; Stratlane provides project management, accredited assessment, AI-assisted evidence analysis, and certificate lifecycle management. The result is rigorous third‑party assurance without unnecessarily long audit timelines.
Are there case studies demonstrating Stratlane’s AI-driven audit success?
Anonymized case summaries show that pairing AI-driven auditing with accredited certification reduced on-site audit time, improved defect detection, and shortened time-to-certification for public clients. Agencies reported quicker identification of document inconsistencies, a higher rate of early corrective actions, and streamlined surveillance cycles through certificate management. Detailed case studies are available from the provider, but anonymized results typically indicate accredited certification with AI augmentation reduces direct audit costs and speeds the delivery of standardized processes. Agencies should consider pilot scopes and request evidence-based summaries to align expectations with program goals.
For agencies ready to proceed, the next steps are usually scoping workshops and a readiness assessment to define timelines and deliverables — turning interest into a concrete certification plan and measurable public-sector outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key challenges public sector organizations face when implementing ISO 9001?
Common challenges include resistance to change, constrained budgets, and the complexity of legacy processes. Staff may be accustomed to existing routines and need time and training to adopt new practices. Limited resources can constrain investment in training, systems, or external support. Aligning ISO requirements with regulatory frameworks and securing stakeholder buy-in can also complicate implementation. Overcoming these hurdles requires visible leadership, clear communication, targeted training, and a firm commitment to continuous improvement.
How long does it typically take for a public sector organization to achieve ISO 9001 certification?
Timelines vary by size, complexity, and existing readiness. In most cases, organizations reach certification in 3 to 12 months. That timeframe covers scoping, gap analysis, corrective action implementation, and the certification audit. Agencies with established quality practices often move faster; those starting from scratch should allow additional time to develop and document processes properly.
What role do employees play in the ISO 9001 certification process?
Employees are central: they operate the processes a QMS aims to control and improve. Their engagement matters for identifying improvement opportunities, documenting day-to-day procedures, and following new workflows. Training and involving staff in QMS design builds a culture of quality and accountability. Frontline teams also provide practical insights into operational challenges and citizen feedback — inputs essential to continuous improvement and certification success.
Can ISO 9001 certification help public sector organizations during crises or emergencies?
Yes. ISO 9001 strengthens crisis response by providing clear processes, defined roles, and established communication paths. The standard’s emphasis on risk-based thinking, documented procedures, and continual improvement helps agencies respond and recover more effectively, keeping critical services running and decisions traceable. That preparedness can shorten recovery times and sustain public confidence during emergencies.
What are the costs associated with obtaining ISO 9001 certification for public sector organizations?
Costs vary widely depending on organization size, process complexity, and current maturity. Typical expenses include staff training, potential consultancy, internal audits, and certification-audit fees. There may also be costs to implement required changes. While upfront investment can be significant, many agencies find that improved efficiency, reduced rework, and better resource allocation offset those costs over time.
How can public sector organizations maintain ISO 9001 certification once achieved?
Maintaining certification requires ongoing commitment. Agencies should schedule regular internal audits, management reviews, and staff training to sustain compliance. Keeping documentation current, responding promptly to nonconformities, and embedding continual improvement into day-to-day operations are essential. Engaging people at all levels and using certificate management services to track surveillance audits and renewals helps preserve certification and improve service delivery over time.
Conclusion
ISO 9001 certification gives public sector organizations a practical, measurable way to raise service quality, improve operational efficiency, and strengthen citizen trust. The standard’s structured approach fosters accountability and transparency while aligning teams around continuous improvement. By combining accredited certification with responsible AI-assisted auditing, agencies can shorten audit cycles, lower costs, and accelerate the benefits of standardized processes. If you’re ready to improve public service delivery, start with a scoping workshop or readiness assessment to map a realistic path to certification with Stratlane.