ISO 14001 Certification: Building Customer Trust Explained

ISO 14001 Certification vs Non-Certified: Trust & Compliance Benefits
ISO 14001 certification and customer trust hinge on verifiable environmental responsibility, transparent reporting, and continuous improvement that demonstrate a company’s commitment beyond unverified claims. IT directors and business leaders face growing pressure from key clients to prove environmental credentials, yet non-certified operations risk legal fines, reputational damage, and lost contracts. This article defines ISO 14001, explains how certification builds stakeholder confidence, compares risks of non-certification, shows why ISO 9001 often joins environmental trust requirements, and offers strategic steps for leveraging both standards. You will learn:
- What ISO 14001 is and how its Environmental Management System (EMS) underpins environmental trust
- How certification enhances compliance, transparency, reputation, and loyalty
- The disadvantages non-certified companies face and the cost of unverified environmental claims
- Why key clients often require ISO 9001 alongside ISO 14001 for holistic quality and sustainability assurance
- Strategic and tactical guidance for business leaders to achieve, integrate, and maintain ISO certifications
- Industry examples showing measurable outcomes on reputation, market access, and customer retention
What Is ISO 14001 and How Does It Establish Environmental Trust?
ISO 14001 is an international standard for Environmental Management Systems (EMS) that defines requirements for a systematic approach to reduce environmental impact, ensuring organisations meet regulatory obligations and foster stakeholder confidence. By formalising processes for planning, implementation, and review, ISO 14001 creates a credible framework that external auditors and clients recognise as proof of environmental responsibility. For example, a manufacturing firm with an EMS can demonstrate pollutant reductions and resource efficiency, reinforcing its brand integrity.
The Role of ISO 14001 in Environmental Compliance - en-gb
ISO 14001 provides a structured framework for organisations to manage their environmental responsibilities, ensuring they meet regulatory requirements and build stakeholder trust through a systematic approach to environmental management. This includes establishing environmental policies, planning, implementation, performance evaluation, and continuous improvement.
International Organization for Standardization, ISO 14001:2015 Environmental management systems — Requirements with guidance for use, (2015)
This standard is the foundation for the article’s discussion of how ISO 14001 establishes environmental trust.
What Are the Core Elements of an ISO 14001 Environmental Management System?
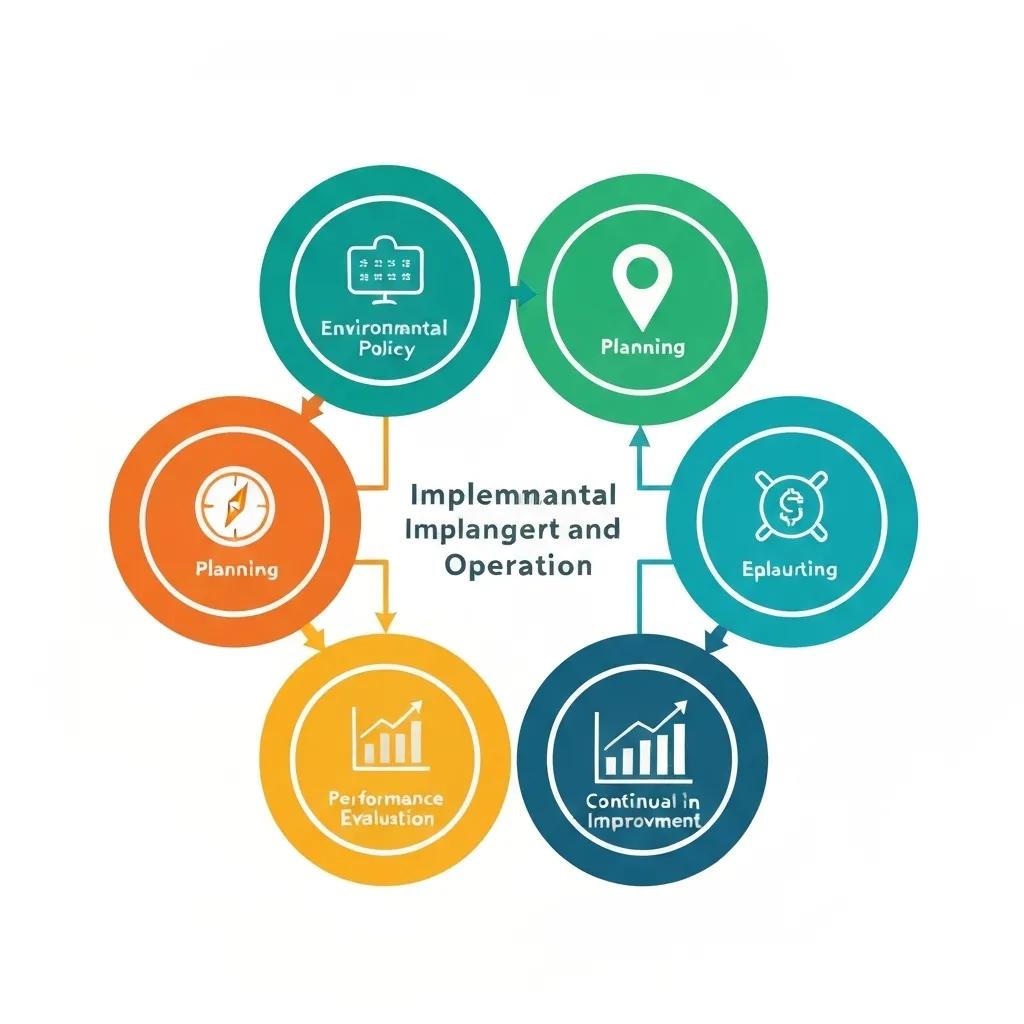
An EMS relies on five interrelated components that work in a continuous improvement cycle:
- Environmental Policy: A public commitment to environmental objectives aligned with corporate goals.
- Planning: Identification of environmental aspects, legal obligations, and risk mitigation measures.
- Implementation and Operation: Defined roles, training, documentation, and operational controls.
- Performance Evaluation: Monitoring, measurement, audit, and management review processes.
- Continual Improvement: Action plans to address non-conformities, optimise resource use, and reduce impact.
Each element creates an auditable trail that external stakeholders can review, establishing a transparent record of environmental performance and risk management.
How Does ISO 14001 Certification Demonstrate Environmental Responsibility?
ISO 14001 certification demonstrates environmental responsibility by validating an organisation’s EMS through an independent audit. Certification bodies review documented processes, on-site controls, and performance data to confirm compliance with international standards. This third-party verification transforms internal practices into external proof of commitment, signalling to customers and regulators that the business adheres to recognised environmental best practices.
Why Is Transparency Important in ISO 14001 Certification?
Transparency in ISO 14001 requires clear reporting of environmental objectives, performance metrics, and non-conformities. Publicly available environmental policies and audit results enable stakeholders to see real data on resource use, waste reduction, and emission levels. This openness converts environmental data into trust signals that reassure clients, investors, and regulators that the organisation is accountable and receptive to scrutiny.
How Does ISO 14001 Drive Continuous Environmental Improvement?
ISO 14001 drives continuous improvement through the Plan–Do–Check–Act (PDCA) cycle, which mandates regular performance evaluations and corrective actions. By analysing audit findings and management reviews, organisations refine processes, set new targets, and enhance resource efficiency. This iterative mechanism not only reduces environmental impact but also demonstrates a proactive stance that strengthens long-term trust and resilience.
How Does ISO 14001 Certification Build Customer and Stakeholder Trust?
ISO 14001 certification enhances customer and stakeholder trust by ensuring compliance, boosting reputation, fostering transparency, and cementing loyalty through verified environmental performance. Certified organisations present a documented commitment to sustainability that resonates with eco-conscious clients and regulatory bodies.
In What Ways Does ISO 14001 Ensure Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation?
ISO 14001’s planning and monitoring requirements ensure legal obligations are identified, tracked, and met. By integrating environmental regulations into the EMS, organisations proactively manage permits, reporting deadlines, and pollutant limits. This systematic approach reduces the risk of fines, legal disputes, and shutdowns, protecting the company’s reputation and operational continuity.
How Does ISO 14001 Certification Enhance Business Reputation and Market Advantage?
ISO 14001 certification improves brand perception by showcasing an organisation’s dedication to reducing environmental impact. In competitive tenders, certified companies often outrank non-certified peers, gaining priority in supplier selection and contract awards. This recognised mark of responsibility differentiates certified businesses in crowded markets and opens doors to new opportunities.
The Impact of ISO 14001 on Market Access - en-gb
ISO 14001 certification can improve brand perception and market advantage, with certified companies often gaining priority in supplier selection and contract awards. This recognised mark of responsibility differentiates certified businesses in crowded markets and opens doors to new opportunities.
Deloitte, “Making the case for ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems,” (2022)
This source provides evidence for the article’s claims about how ISO 14001 certification can enhance business reputation and market advantage.
What Role Does Transparency Play in Strengthening Stakeholder Confidence?
Transparent EMS reporting provides stakeholders with clear, auditable data on environmental objectives, energy savings, and emission reductions. Sharing KPI dashboards, audit summaries, and improvement plans signals a willingness to collaborate and accept accountability. This transparency nurtures trust among investors, communities, and key clients who seek assurance of genuine environmental stewardship.
How Does Certified Environmental Performance Influence Customer Loyalty?
Verified environmental achievements—such as waste diversion rates, water conservation, or CO₂ emission reductions—resonate with customers who prioritise sustainability. Data-driven milestones communicated through sustainability reports and marketing materials reinforce loyalty, as clients prefer suppliers whose values align with their own. Over time, demonstrable environmental performance becomes a core driver of repeat business and referrals.
What Are the Risks and Disadvantages of Operating Without ISO 14001 Certification?
Non-certified organisations face eroded trust, higher liabilities, and restricted market access because unverified environmental claims lack credibility. Without an EMS framework, companies struggle to prove compliance, leaving them vulnerable to fines, brand damage, and lost business.
How Does Lack of Certification Affect Verifiable Environmental Commitment?
Without ISO 14001, environmental policies remain internal aspirations rather than audited facts. Stakeholders cannot verify sustainability claims, leading to scepticism and reduced confidence. This lack of independent validation makes it difficult for clients and regulators to trust environmental performance reports.
What Legal and Reputational Risks Do Non-Certified Companies Face?
Non-certification exposes businesses to regulatory fines, legal actions, and public scrutiny when environmental incidents occur. Failure to track and report emissions or waste can result in costly penalties and negative media coverage. These reputational setbacks erode customer trust and discourage investor support.
How Does Non-Certification Limit Market Access and Client Acquisition?
Many procurement frameworks and supply-chain mandates require proof of ISO 14001 registration. Non-certified suppliers are often disqualified from tenders or considered higher-risk partners. This barrier restricts access to key clients, especially in industries where environmental criteria are mandatory.
What Are Common Misconceptions About Non-Certified Environmental Claims?
Businesses sometimes assume that voluntary sustainability reports suffice, but without external audit they risk accusations of greenwashing. Misleading claims about carbon neutrality or zero waste fall flat without a certified EMS to track and verify progress. Genuine responsibility requires documented systems and continuous improvement under ISO 14001 guidelines.
Why Is ISO 9001 Certification Often Required by Key Clients Alongside ISO 14001?
ISO 9001 certification is frequently mandated by major clients to guarantee quality management practices, complementing ISO 14001’s environmental trust by ensuring consistency, reliability, and customer satisfaction across products and services.
What Is ISO 9001 and How Does It Complement ISO 14001?
ISO 9001 specifies requirements for Quality Management Systems (QMS) focused on meeting customer needs and enhancing satisfaction. When combined with ISO 14001, organisations demonstrate holistic responsibility: environmental performance and quality consistency. This dual-system synergy reassures clients that both sustainability and product/service excellence are managed systematically.
How Does ISO 9001 Certification Ensure Quality and Client Satisfaction?
Through documented processes for design, production, delivery, and feedback, ISO 9001 certification ensures that customer requirements are understood, fulfilled, and monitored. Regular internal audits and management reviews identify non-conformities, initiate corrective actions, and drive process improvements that enhance reliability and client satisfaction.
Why Do Key Clients Prioritize ISO 9001 Certification in Supplier Selection?
Key clients often require ISO 9001 to minimise supply-chain risk, ensure predictable quality, and meet regulatory obligations. Certification proves that a supplier has robust controls for product consistency, defect reduction, and customer communication, reducing warranty claims and service disruptions.
How Do ISO 14001 and ISO 9001 Together Build Holistic Business Trust?
The combined implementation of ISO 14001 and ISO 9001 creates an Integrated Management System (IMS) that aligns environmental and quality objectives. This unified framework optimises resources, reduces duplication, and presents a single, credible narrative of responsible operations—enhancing stakeholder confidence across environmental and quality dimensions.
The Benefits of ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 Integration - en-gb
The integration of ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 creates an Integrated Management System (IMS), which aligns environmental and quality objectives, optimising resources and presenting a credible narrative of responsible operations. This unified approach enhances stakeholder confidence across environmental and quality dimensions.
Casadesus, M., & Karapetrovic, S., “ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015: A comparative analysis,” Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, (2017)
This research supports the article’s claims about the benefits of combining ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 for holistic business trust.
How Can Business Leaders Strategically Leverage ISO Certifications to Enhance Trust and Competitive Advantage?

By adopting ISO 14001 and ISO 9001, business leaders signal operational excellence, mitigate risk, and meet stakeholder expectations, converting standards into strategic assets that drive differentiation and growth.
What Are the Strategic Benefits of Embracing ISO 14001 and ISO 9001 Certifications?
- Operational Efficiency – Standardised processes reduce waste, save costs, and improve resource utilisation.
- Market Access – Certification unlocks tenders, preferred supplier status, and new customer segments.
- Risk Mitigation – Systematic audit and review processes minimise legal, environmental, and quality-related liabilities.
- Reputation Enhancement – Third-party validation strengthens brand image and positions the company as an industry leader.
These benefits coalesce into measurable ROI through increased contract wins, reduced non-conformities, and improved stakeholder relations.
How Can IT Directors and Founders Use ISO Certifications to Meet Stakeholder Expectations?
IT directors and founders can align certification objectives with corporate sustainability and quality roadmaps. Integrating EMS and QMS data into executive dashboards ensures visibility of compliance KPIs, environmental metrics, and customer feedback. This real-time insight supports strategic decisions, investor reporting, and continuous stakeholder engagement.
What Steps Should Businesses Take to Achieve and Maintain ISO Certification?
- Conduct a gap analysis of existing processes against ISO requirements.
- Develop or update environmental and quality policies with leadership commitment.
- Document procedures, responsibilities, and controls in an EMS/QMS manual.
- Train employees on roles, risks, and objectives.
- Perform internal audits, management reviews, and corrective actions.
- Engage an accredited certification body for external audit and registration.
- Implement a continual improvement cycle with periodic re-certification.
By following these steps, companies build structured, auditable systems that sustain certification and drive performance.
How Do Certified Environmental and Quality Management Systems Mitigate Business Risks?
Certified systems identify, assess, and control environmental and quality hazards before they escalate. Audit findings feed into risk registers that align with corporate governance and insurance requirements. This risk-based approach prevents costly incidents, protects reputation, and ensures business continuity under changing regulatory landscapes.
What Are Industry Examples and Case Studies Demonstrating the Impact of ISO 14001 Certification on Trust?
Real-world examples show how ISO 14001 certification elevates company profiles, improves compliance, and delivers measurable outcomes in trust and market growth.
How Have Leading Companies Improved Reputation and Compliance Through ISO 14001?
| Organisation | Improvement Area | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung Electronics | Energy consumption | 18% reduction in nationwide energy use by 2020 |
| Dell Technologies | Waste diversion | Achieved zero waste to landfill at five sites in 2021 |
| Toyota Motor Corp | Emission tracking | 25% cut in CO₂ emissions per vehicle by 2025 goal |
These metrics illustrate how certified EMS frameworks drive both environmental performance and positive brand narratives that resonate with stakeholders.
What Lessons Can Be Learned from Businesses That Failed to Certify?
Organisations that delayed certification often faced regulatory fines, contract losses, and public backlash during environmental incidents. A mid-sized chemical plant without an EMS incurred £250k in penalties due to uncontrolled discharges, losing major clients concerned about supply-chain risk. This highlights the cost of unverified environmental management.
How Does ISO 14001 Certification Influence Supply Chain Transparency and Client Confidence?
In sectors like electronics and automotive, OEMs increasingly require ISO 14001 from suppliers to ensure sustainable sourcing. A UK electronics assembler reported a 30% increase in RFQs after achieving certification, as procurement teams favoured transparent, certified partners. This demonstrates how EMS credentials translate into tangible market advantage.
What Are the Measurable Outcomes of Certification on Customer Loyalty and Market Growth?
- 15% higher customer retention in sustainability-focused markets
- 8% revenue growth in new green contracts
- 12% reduction in insurance premiums due to lower incident rates
These figures confirm that verified environmental management yields both trust and financial returns.
Securing ISO 14001 certification builds a foundation of environmental trust that non-certified peers cannot match, while integrating ISO 9001 ensures quality demands from key clients are met. Stratlane’s ISO Certification Consulting and Implementation Services guide business leaders through gap analysis, EMS/QMS design, auditing, and continual improvement, enabling organisations to exceed stakeholder expectations. By embracing both standards, IT directors and founders transform compliance into strategic advantage, protect reputation, and unlock new markets. Certified environmental and quality management systems mitigate risks, enhance operational efficiency, and foster lasting client confidence for sustainable growth.